Manual control and testing
Contents
Manual control and testing
All functions on Recore are meant to be controlled from a graphical user interface such as OctoPrint, Fluid or Mainsail etc. This in turn in controlled by Klipper. Sometimes it can be beneficial to get low level access to certain functions and test things directly on the command line. This section is meant to give an overview of what capabilites are available from the command line (SSH/terminal).
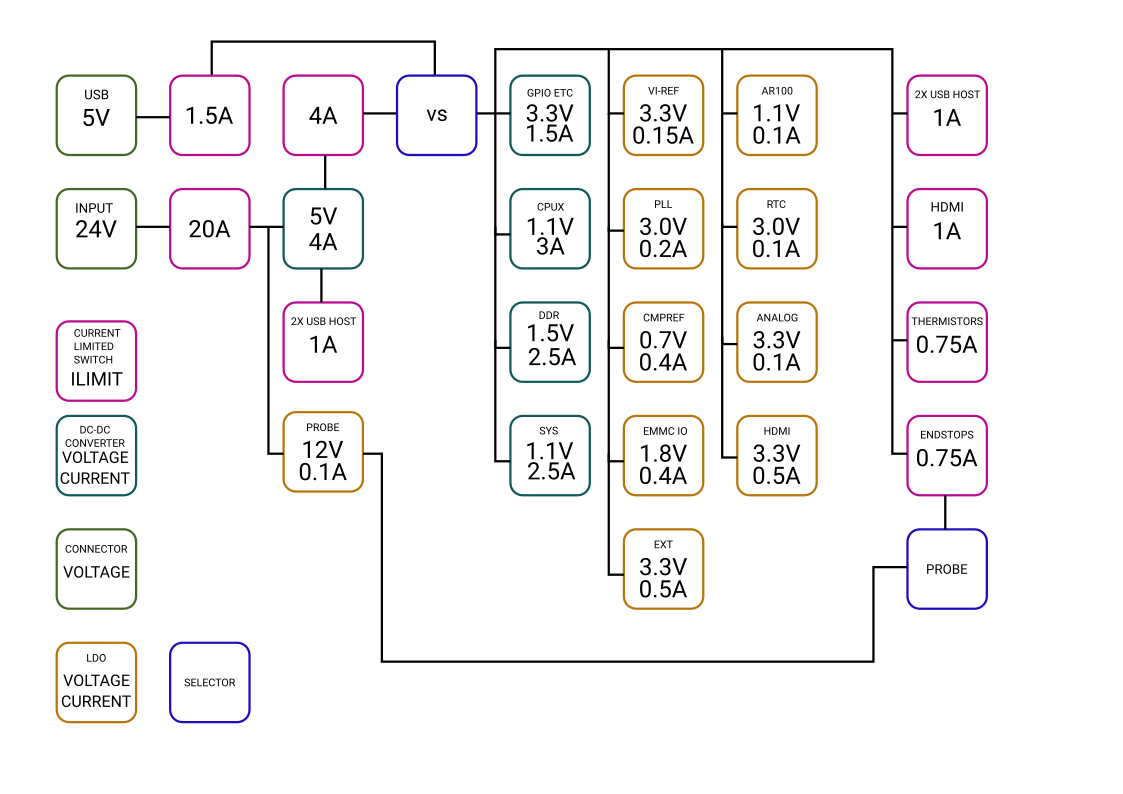
Power domain overview
Power domains
There are 9 power domains around the board controlling voltage on different pins:
- Input power controls power to 4 high power outputs, the 4 fans and the 6 stepper drivers. This input has current monitoring, fast acting over current protection, voltage monitoring, temperature monitoring and reverse polarity protection.
- Thermo couple power Controls +5V/1A output to the ADCs. This can be used for turning on power to the analog pins.
- End stop power Controls +5V/1A output on the six endstops. Ganged. ES0 can be switched to have 12V output. The 12V output has a
100mA internal current limit.
- 4 USB host power domains Controls 5V/1A current output to the usb host connectors. These are turned on by u-boot.
- HDMI 5V output Controls the 5V/1A HDMI output. Turned on by u-boot.
Input stage
Reset over current protection and set it in "one-shot" mode.
gpioset 1 164=0 gpioset 1 164=1
The over current protection can also be set in "transparent" mode, where the current alarm will be reset automatically. Note that this is a bad idea for general operation, only use for testing.
gpioset 1 164=0
Enable 24V input
gpioset 1 165=0
End stop 5V /12V
End stop 0 to 4 has a programmable +5V output voltage. End stop 5 has +5V or +12V selectable.
To enable +5V on ES 1...5
gpioset 1 162=1
To disable again
gpioset 1 162=0
To switch to 12V output on ES0
gpioset 1 160=1
To disable again
gpioset 1 160=0
End stops values
To see what value the end stops have
gpioget 1 228 # ES 5 gpioget 1 229 gpioget 1 230 gpioget 1 231 gpioget 1 232 gpioget 1 233 # ES 0
TMC2209
In window/shell 1:
stty -F /dev/ttyS2 raw -echoe -echo xxd -c 4 /dev/ttyS2
In window/shell 2:
echo -n -e '\x5\x0\x6\x6F' > /dev/ttyS2
The return should be along the lines of
00000000: 0500 066f ...o 00000004: 05ff 0620 ... 00000008: 0001 4058 ..@X
To check that no errors are reported by the steppers write this on the command line. If a "1" shows up, that is an indication that the motor is reporting an error.
gpioget 1 128 gpioget 1 129 gpioget 1 130 gpioget 1 131 gpioget 1 132 gpioget 1 133
STM32F031
There is a small firmware to test all functionality that is controlled by the STM32F031 chip on the board. Once uploaded to the board using the flash script, the firmware will turn on all LEDs it controls and send back ADC readings.
To flash this firmware to the STM32:
gpioset 1 197=1 gpioset 1 196=0 stm32flash -i -196,196 -w Sumato-f031.bin -v -g 0x00 /dev/ttyS1 gpioset 1 197=0 stm32flash -i -196,196 /dev/ttyS1
To see the ADC readings:
stty -F /dev/ttyS3 38400 raw cat /dev/ttyS3
You should see something like
ADC T0: 0 ADC T1: 0 ADC T2: 0 ADC T3: 0 ADC U: 2338 ADC I: 0 ADC TB: 3417
The following one-liners assumes gawk is installed.
Reading Current
There is board current reading implemented in OctoPrint. The current shunt resistor is 1 mOhm, the amplifier is 20 times, the vref is 3.3V, so we get: (adc_val/4096*3.3)*1000/20 = (adc_val/4096)*165
If the testing firmware is installed on the STM32, you can convert the current (as in amps) reading to something useful like this:
cat /dev/ttyS4 | awk '/I:/ { printf "scale=4; (%i/4096)*165\n", $3; fflush(); }' | bc -l
Current limit programming
The current limit must be set in the device tree by programming the voltage on dldo2. dldo2 can have values from 0.7 V to 3.4 V. Setting the voltage level to 3.4 V effectively disables the fast acting current limit. Setting it to the lowest value gives an over current limit of 35 A.
Reading Board Temperature
To see the temperature readings, try this :
export beta=4327
cat /dev/ttyS1 | awk '/TB:/ { printf "scale=4; 4327/l( (4700/((3.3/(3.3*%i/4096))-1.0))/0.05306820342563400000) -273.15\n", $3; fflush(); }' | bc -l | awk '{print strftime("%k:%M:%S"), $0; fflush();}'
Reading Input Voltage
To see voltage on the input, it can be converted like this:
exec 4</dev/ttyS4 5>/dev/ttyS4
echo -n ";A4;" >&5
read -t1 reply <&4
echo $reply | awk '{ printf "scale=4; (%i/4096)*3.3*((100+10)/10)\n", $4; fflush(); }' | bc -l
Thermistor inputs
To enable pull-up on input for using thermistors for temperature measurements:
gpioset 1 202=1 gpioset 1 203=1 gpioset 1 204=1 gpioset 1 205=1
Setting Op-amp gain to 1:
gpioset 1 100=0 gpioset 1 235=0 gpioset 1 145=0 gpioset 1 34=0
Setting Op-amp gain to 100:
gpioset 1 100=1 gpioset 1 235=1 gpioset 1 145=1 gpioset 1 34=1
Adding a 0.33 V offset to the input:
gpioset 1 192=1 gpioset 1 193=1 gpioset 1 194=1 gpioset 1 200=1
Do not add 0.33 V offset to the input:
gpioget 1 192 gpioget 1 193 gpioget 1 194 gpioget 1 200
In the device tree file, the gpio/ldos must be set to gpio input:
&gpio0_ldo {
function = "gpio_in";
};
Thermocouple input
Either a thermocouple or a thermistor can be used as input on the T0-T3 inputs.
Bias
The thermocouple is set up to have a Bias of 0.7V/100 on the input which enables negative values (lower than the board temperature) as input to the ADCs. With the input short circuited, the bias can be recorded. Typical values are 750 This needs to be subtracted from the result.
Cold junction compensation
Another important aspect is cold junction compensation. There is a thermistor connected on the board close to the thermocouple inputs which can be used to measure the temperature close to the input junction. This temperature must be added in software.
The connected thermistor is a TDK NTCG104EF104FT1X The connected Thermocouple has a (25/100) beta value of 4327 K and a (25/85) beta value of 4308 K. The 25/85 beta value is what is used in Klipper.
In order to use the inputs for thermocouple, the pull-up-down resistors must be set to pull-down:
gpioset 1 102=0 gpioset 1 120=0 gpioset 1 160=0 gpioset 1 161=0
Also, the op-amp needs a gain of 100:
gpioset 1 100=0 gpioset 1 235=0 gpioset 1 145=0 gpioset 1 34=0
Finally, the input bias needs to be enabled. The following LDOs needs to be enabled:
reg_ldo_io0 reg_ldo_io1 reg_dldo3 reg_dldo4